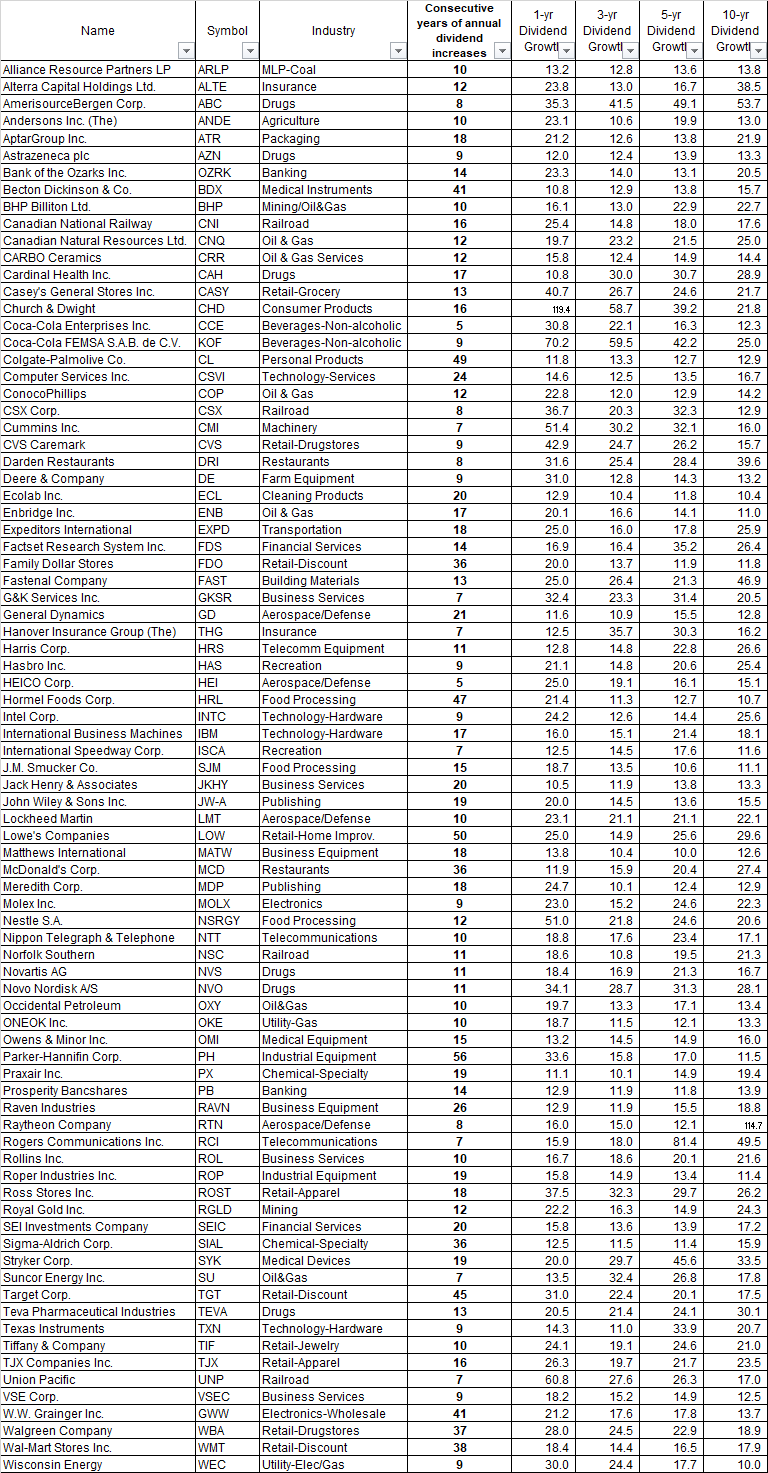
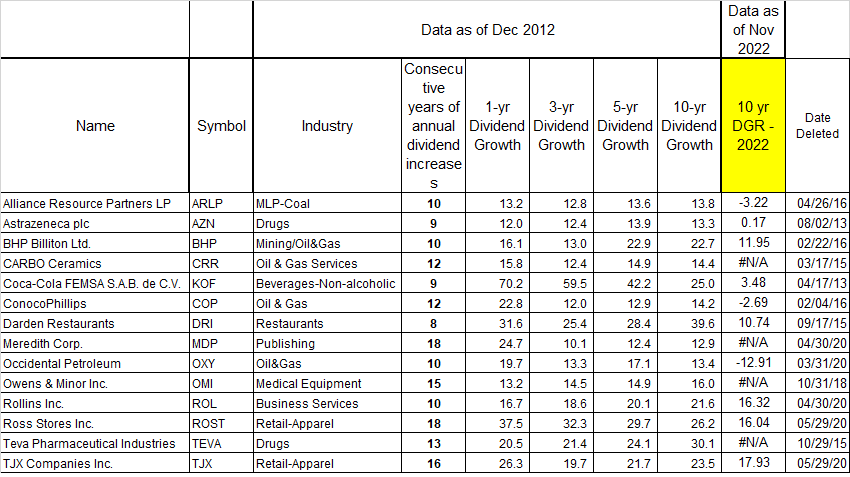
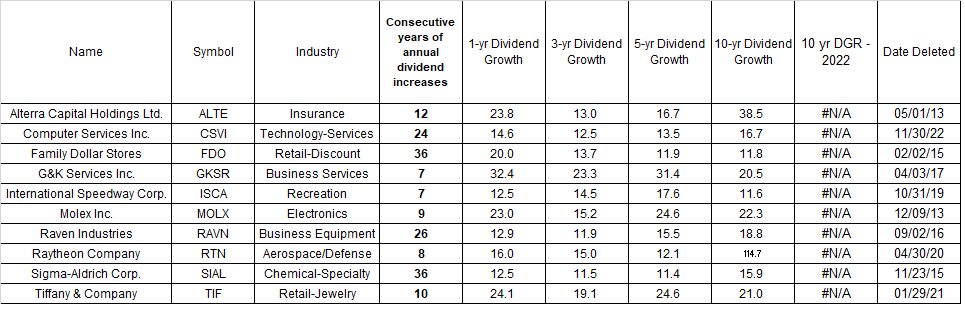
The Dow Jones Industrials Average Index was launched in 1896 with 12 companies. It has tracked the performance of leading US companies for over 125 years.
In 1916 it increased to 20 stocks and in 1928 to 30 stocks.
Where are the original 12 companies today?
I went ahead and used the 2013 edition of "Stocks For the Long Run" and data from Global Financial Data through 2020 to trace the histories of each company. Enjoy!
American Cotton Oil became Best Food in 1923, Corn Products Refining in 1958, and finally CPC International in 1969—a major food company with operations in 58 countries. In 1997, CPC spun off its corn-refining business as Corn Products International and changed its name to Bestfoods. Bestfoods was acquired by Unilever in October 2000 for $20.3 billion. Unilever (UN), which is headquartered in the Netherlands, has a current market value of $115 billion. (as of 2013)
American Sugar became Amstar in 1970 and went private in 1984. In September 1991 the company changed its name to Domino Foods, Inc., to reflect its world-famous Domino line of sugar products.
American Tobacco changed its name to American Brands (AMB) in 1969 and to Fortune Brands (FO) in 1997, a global consumer products holding company with core businesses in liquor, office products, golf equipment, and home improvements. American Brands sold its American Tobacco subsidiary, including the Pall Mall and Lucky Strike brands, to one-time subsidiary B.A.T. Industries in 1994. In 2011 Fortune Brands changed its name to Beam Inc (BEAM), which operates as a distribution company in the spirits industry. The market value is $9 billion. (as of 2013)
Chicago Gas became Peoples Gas Light & Coke Co. in 1897 and then Peoples Energy Corp., a utility holding company, in 1980. Peoples Energy Corp. (PGL) was bought by WPS Resources and changed its name in 2006 to Integrys Energy Group (TEG). It has a market value of $4.1 billion. PGL was a member of the Dow Jones Utility Average until May 1997.
Distilling & Cattle Feeding went through a long and complicated history. It changed its name to American Spirits Manufacturing and then to Distiller’s Securities Corp. Two months after the passage of Prohibition, the company changed its charter and became U.S. Food Products Corp. and then changed its name again to National Distillers and Chemical. The company became Quantum Chemical Corp. in 1989, a leading producer of petrochemicals and propane. Nearing bankruptcy, it was purchased for $3.4 billion by Hanson PLC, an Anglo-American conglomerate. It was spun off as Millennium Chemicals (MCH) in October 1996. Lyondell Chemical (LYO) bought Millennium Chemicals in November 2004. In 2007 Lyondell was taken over by the Dutch firm that renamed itself Lyondell Basell Industries (LYB). The current market value of Lyondell Basell is $28 billion. (as of 2013)
General Electric (GE), founded in 1892, is the only original stock still in the Dow Industrials. GE is a huge manufacturing and broadcasting conglomerate that owns NBC and CNBC. Its market value of $218 billion is the third-highest capitalization stock in the United States. (as of 2013)
Laclede Gas (LG) changed its name to Laclede Group, Inc., and it is a retail distributor of natural gas in the St. Louis area. The market value is $900 million. (as of 2013)
National Lead (NL) changed its name to NL Industries in 1971, and it manufactures products relating to security and to precision ball bearings, as well as titanium dioxide and specialty chemicals. The market value is $520 million. (as of 2013)
North American became Union Electric Co. (UEP) in 1956, providing electricity in Missouri and Illinois. In January 1998, UEP merged with Cipsco (Central Illinois Public Service Co.) to form Ameren (AEE) Corp. The market value is $72 billion. (as of 2013)
Tennessee Coal and Iron was bought out by U.S. Steel in 1907, and it became USX-U.S. Steel Group (X) in May 1991. In January 2002, the company changed its name back to U.S. Steel Corp. U.S. Steel has a market value of $3 billion. (as of 2013)
U.S. Leather, one of the largest makers of shoes in the early part of this century, liquidated in January 1952, paying its shareholders $1.50 plus stock in an oil and gas company that was to become worthless.
U.S. Rubber became Uniroyal in 1961, and it was taken private in August 1985. In 1990 Uniroyal was purchased by the French company Michelin Group, which has a market value of $15 billion. (as of 2013)
Conclusion:
This is fascinating to me for several reasons.
First, it is fascinating to trace how a group of select individual corporations have done over a long period of time. There may be some lessons to be applied in the construction of our own portfolios. It is fascinating to see how many companies have survived in one form or another today, and have made money to investors. That also does not include dividends, which would have further turbocharged results.
Second, I have always wanted to test how an investor in US equities in 1896 would have done, if they had followed the coffee can approach to portfolio construction.
Imagine a situation where passive investor had selected an equal weighted portfolio of each of those 12 companies in 1896, and donated them to a charitable institution. They asked the foundation to never sell any stock and to never re-balance. That charity would have been set for 125 years. It would have been able to "live off dividends" in a way, and provide value to those in need for a long period of time, while also enjoying growth in assets under management.
Third, it is fascinating to trace further how much change there has been in the past decade, since that was posted in 2013. Some folks have extrapolated that change into stating that everything is subject to creative destruction. I believe that companies are more stable and adaptable than the popular narratives today.
A company may die in a certain period of time, but in the meantime, it may spin-off assets that would thrive and/or it would pay dividends along the way. A company may also get acquired before it meets its maker, which prolongs the shareholding of stockholders.
A company may also add or remove subsidiaries, merge with and spin-off companies. It may benefit from creative disruption and technological changes, or it may have the type of business that serves a basic human need that may last a while.
Relevant Articles:
- Time in the market is your greatest ally in investing
- The Perfect Dividend Portfolio